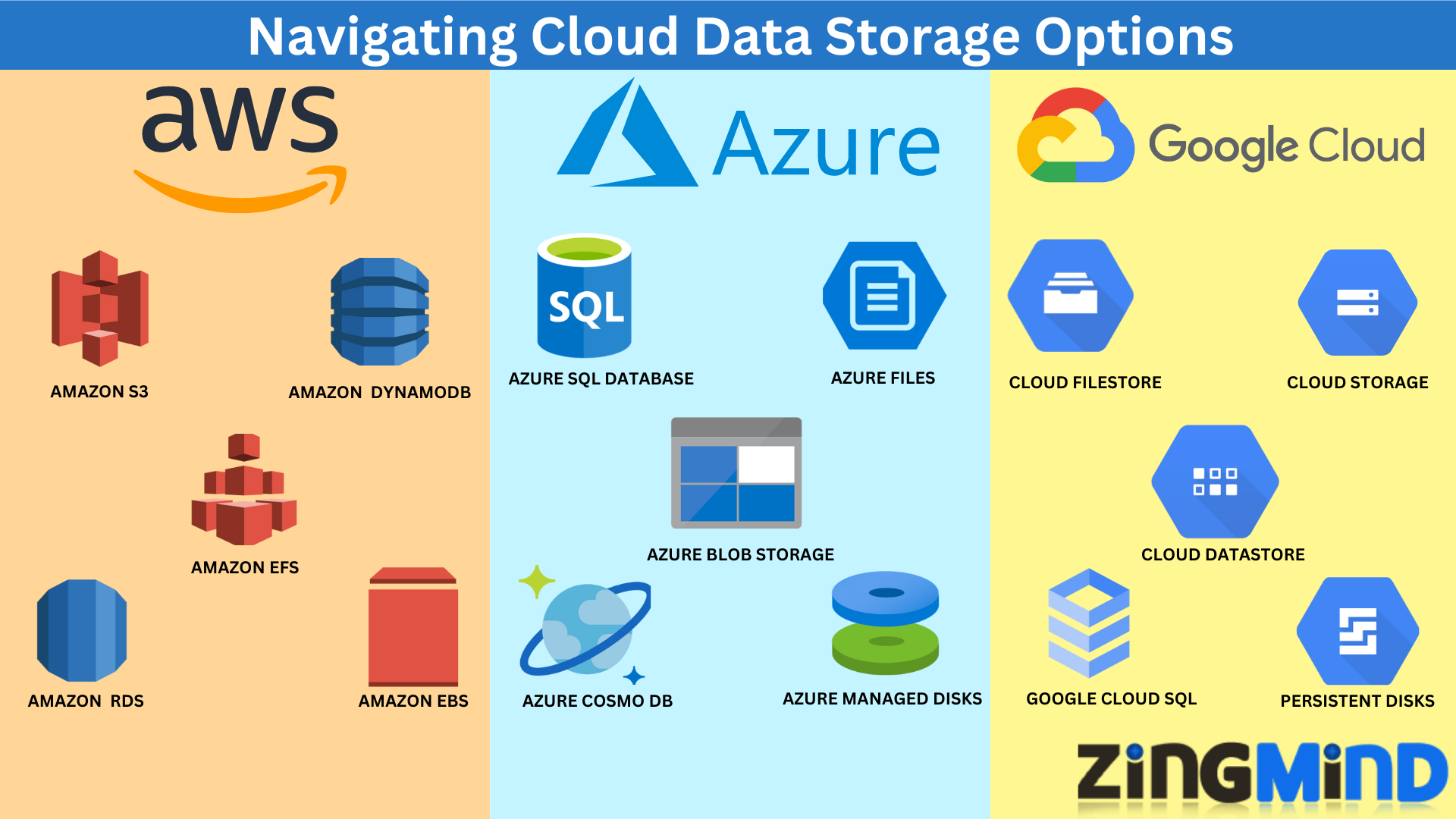
Navigating Cloud Data Storage Options: Features, Performance, and Cost Comparison across AWS, GCP, and Azure
Cloud computing has revolutionized data storage, offering an array of options designed to meet diverse needs. But navigating the vast landscape of cloud data storage options can be a daunting task. With numerous providers and a multitude of features to consider, it’s important to understand the nuances of each option before making a decision.This article delves into the intricacies of cloud data storage, examining key solutions available across major platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). By comprehending the technical strengths, use cases, and associated costs of each solution, businesses can make informed decisions tailored to their specific data storage requirements.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Data Storage Solution
Before we dive into the comparison, let’s briefly discuss why choosing the right data storage solution is paramount:
- Scalability: Data storage needs vary over time. Scalability allows you to adjust your storage capacity as your data grows. A flexible storage solution ensures that you can meet your requirements without overpaying for unused resources.
- Performance: The speed at which data can be read, written, and processed is crucial, especially for applications that demand low latency and high throughput.
- Reliability and Durability: Data loss is not an option. Cloud providers offer various redundancy and backup mechanisms to ensure your data remains safe and accessible.
- Cost-Efficiency: Cloud storage costs can quickly add up, so optimizing your storage strategy is essential. Understanding pricing models and making cost-effective choices can significantly impact your budget.
Exploring Cloud Data Storage Solutions
1. Object Storage
Amazon S3 (AWS)
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a foundational component of AWS’s storage offerings, providing scalable, durable, and highly available object storage. Key features include:
- Storage Classes: Multiple storage classes like Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, and Glacier cater to various access patterns and cost considerations.
- Cost Control: Granular cost control based on storage class, data retrieval frequency, and region.
- Security: Robust security features, including server-side encryption, access control lists (ACLs), and bucket policies.
- Durability: High durability with data replication across multiple Availability Zones.
Google Cloud Storage (GCP)
Google Cloud Storage offers a versatile object storage solution with a focus on performance and global availability. Key features include:
- Storage Classes: Multiple classes, including Standard, Nearline, and Coldline, suit different storage needs.
- Competitive Pricing: Pricing influenced by storage class, data retrieval, and geographic location.
- Security: Encryption at rest by default, allowing customers to manage their encryption keys.
- Redundancy: Data redundancy across locations and regions enhances data durability.
Azure Blob Storage (Azure)
Azure Blob Storage is Microsoft’s equivalent to object storage, delivering scalable, secure, and cost-effective storage for various applications. Key features include:
- Storage Tiers: Multiple storage tiers, including Hot, Cool, and Archive, designed for different access patterns.
- Flexible Pricing: Pricing flexibility based on storage tier, data egress, and redundancy options.
- Security: Encryption at rest and in transit, with Azure Private Link for secure data access.
- Access Control: Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for precise access control.
2. File Storage
Amazon EFS (AWS)
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) offers fully managed, scalable file storage that can be shared across multiple instances. Key features include:
- Dynamic Scaling: Scalability based on storage size and data transfer requirements.
- Access Control: Integration with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for access control.
- Use Cases: Ideal for applications with collaborative workloads and shared data requirements.
Google Cloud Filestore (GCP)
Google Cloud Filestore is a managed Network File System (NFS) service designed for high-performance file storage. Key features include:
- Managed NFS: NFS-based file storage with pricing based on storage capacity and throughput.
- Compatibility: Excellent compatibility with Linux applications and workloads.
- Performance: Suitable for applications requiring high I/O performance.
Azure Files (Azure)
Azure Files provides fully managed SMB file shares for Windows and Linux clients. Key features include:
- Pricing Model: Pricing based on storage usage and data egress.
- Integration: Integration with Azure Active Directory for secure access control.
- Use Cases: Ideal for enterprises with Windows-based applications and data-sharing needs.
3. Block Storage
Amazon EBS (AWS)
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) offers block-level storage for EC2 instances. Key features include:
- Volume Types: Various volume types, including General Purpose, Provisioned IOPS, and Cold HDD.
- Pricing Variability: Pricing varies based on volume type and provisioned IOPS.
- Performance: Ideal for applications requiring high-performance block storage.
Google Persistent Disks (GCP)
Google Persistent Disks provide block storage for Google Compute Engine instances. Key features include:
- Disk Types: Options for Standard HDD and SSD disks.
- Pricing Structure: Pricing based on disk capacity and type.
- Performance and Scalability: Excellent performance and scalability for virtual machines.
Azure Managed Disks (Azure)
Azure Managed Disks provide scalable and highly available block storage for Azure Virtual Machines (VMs). Key features include:
-
- Disk Types: Multiple disk types, including Standard HDD, Standard SSD, and Premium SSD.
- Pricing Flexibility: Pricing determined by disk type and size.
- Versatility: Ideal for VMs with varying performance requirements.
4. Database Services
Amazon RDS (AWS)
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) offers managed relational databases with support for various database engines such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and more. Key features include:
- Managed Databases: Fully managed database instances with automatic backups and scaling options.
- Pricing Factors: Pricing influenced by instance type, storage, and data transfer.
- Use Cases: Ideal for organizations requiring a managed relational database solution.
Google Cloud SQL (GCP)
Google Cloud SQL offers managed databases for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. Key features include:
- Managed Databases: Fully managed database instances with automated backups, updates, and scaling.
- Pricing Model: Pricing determined by instance type, storage, and data transfer.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interface and seamless integration with other Google Cloud services.
Azure SQL Database (Azure)
Azure SQL Database is a managed SQL database service offering different performance levels. Key features include:
- Managed SQL Databases: Managed database instances with automated backups, patching, and scaling.
- Pricing Flexibility: Pricing depends on the compute tier and storage selected.
- Integration: Integration with other Azure services for comprehensive solutions
5. NoSQL Databases
Amazon DynamoDB (AWS)
Amazon DynamoDB is a serverless NoSQL database service known for its scalability and performance. Key features include:
- Serverless: No servers to manage, with automatic scaling based on demand.
- Pricing Model: Charges based on provisioned throughput and storage.
- Scalability: Seamlessly scales to accommodate changing workloads.
Google Cloud Firestore (GCP)
Google Cloud Firestore is a scalable NoSQL database offering for web, mobile, and server applications. Key features include:
- Serverless: No infrastructure management required, with automatic scaling.
- Pricing Structure: Pricing depends on document reads, writes, deletes, and storage.
- Real-time Data: Supports real-time data synchronization for collaborative applications.
Azure Cosmos DB (Azure)
Azure Cosmos DB is a globally distributed NoSQL database known for its low-latency, multi-model capabilities. Key features include:
- Global Distribution: Data can be replicated globally for low-latency access.
- Pricing Model: Costs vary by request units (RU), storage, and data transfer.
- Multi-Model Support: Supports various data models, including document, key-value, graph, and column-family.
Cost Considerations and Decision-Making
When choosing a storage solution, cost is a significant factor. Consider these aspects:
- Storage Type: Object storage is cost-effective for large-scale data, while databases offer better performance for structured data.
- Access Patterns: File storage suits collaborative workloads, while block storage is ideal for I/O-intensive applications.
- Data Lifecycle: Use archival storage for infrequently accessed data to save costs.
Effective data storage in the cloud requires a comprehensive understanding of available options, performance characteristics, and associated costs. By analyzing your data requirements, access patterns, and budget constraints, you can tailor your storage strategy to maximize efficiency and minimize expenditure. AWS, GCP, and Azure offer versatile storage solutions, each with its strengths. Consider your unique business needs to choose the cloud storage platform that best aligns with your goals and objectives. Whether you prioritize performance, cost-efficiency, or a mix of both, the cloud provides a range of storage solutions to empower your data-driven journey in the digital era.


